Ever lean on a railing and think, "Wow, this is a sturdy railing"? Probably not. But someone, somewhere, thought very hard about that railing. They thought about its height, its strength, the materials it's made of, and a whole bunch of other things you’ve probably never considered. Why? Because handrails aren't just aesthetic additions; they're crucial safety features governed by building codes.
These codes, often a dense thicket of regulations, might seem like overkill. But imagine a world without them. Staircases become treacherous, balconies precarious, ramps risky. Handrail regulations exist to prevent accidents and ensure accessibility, providing a vital safeguard for everyone from toddlers to the elderly.
The history of handrail codes is interwoven with the history of building itself. As structures became taller and more complex, the need for safety measures grew. Early codes were rudimentary, but they laid the foundation for today’s more comprehensive regulations. Over time, these codes evolved, responding to tragic accidents, advancements in construction techniques, and a growing understanding of human factors.
One of the central issues surrounding handrail building codes is their complexity. Navigating the various requirements—height, clearance, load capacity, materials—can be daunting for even experienced builders. This complexity stems from the need to address a wide range of building types, from single-family homes to multi-story commercial buildings. Finding a balance between prescriptive and performance-based codes is an ongoing challenge.
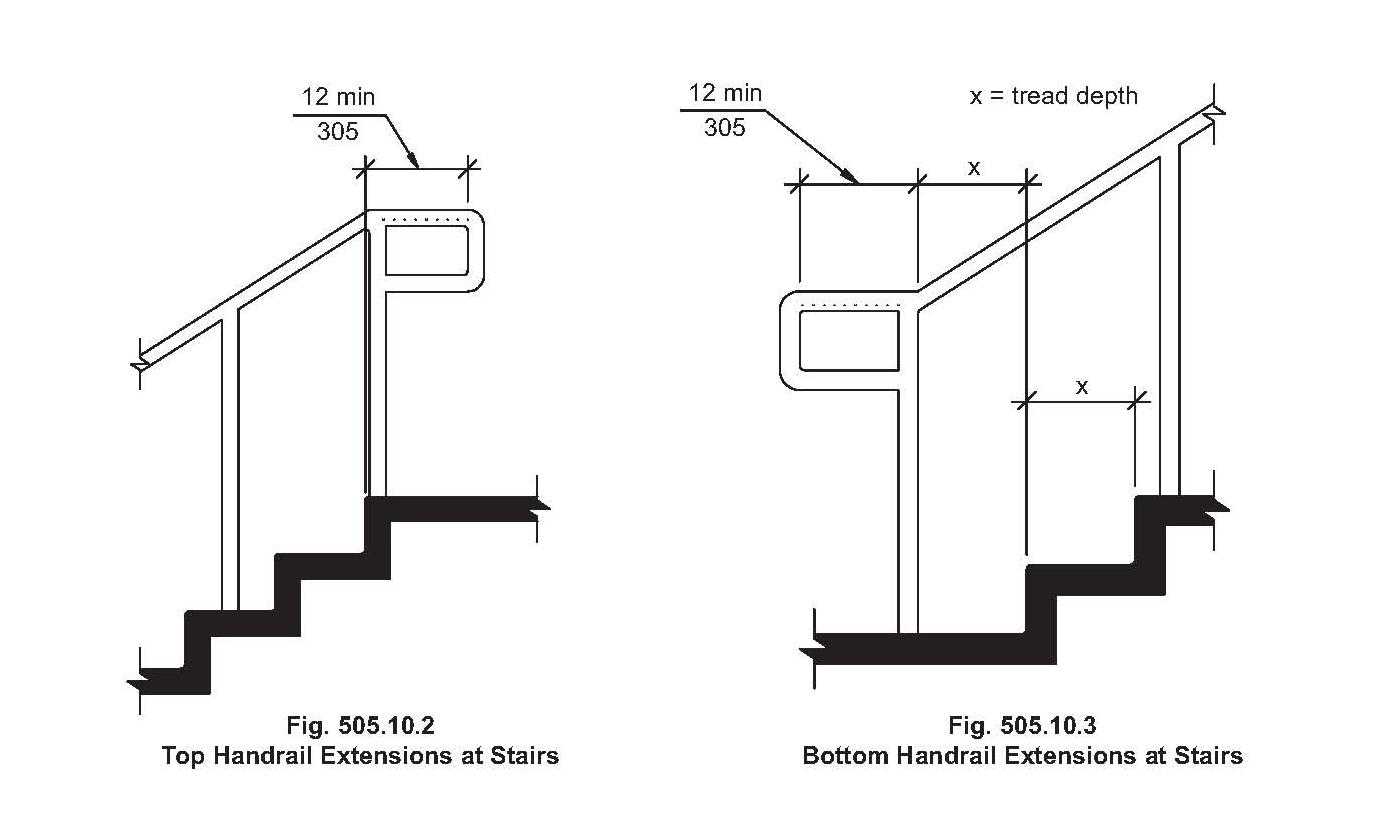
Essentially, handrail building codes aim to provide safe and accessible handrails in all buildings. “Safe” means capable of supporting the anticipated load, resistant to failure, and designed to minimize the risk of falls. “Accessible” means usable by people with disabilities, considering factors like handrail height and graspable shape. A simple example: a handrail too low offers insufficient support, while one too high is unreachable for shorter individuals.
Implementing compliant handrails brings numerous benefits. First, enhanced safety: properly constructed handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls, preventing injuries and even fatalities. Second, improved accessibility: handrails allow people with mobility limitations to navigate stairs and ramps safely and independently. Third, increased property value: compliance with building codes demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety, making a property more attractive to potential buyers.
Ensuring compliance requires a step-by-step approach. First, consult the relevant building codes for your area. These codes vary depending on location and building type. Second, carefully measure and plan your handrail installation, considering all requirements, including height, clearance, and load capacity. Third, choose appropriate materials and construction techniques that meet the code specifications. Finally, have a qualified inspector verify that the installation complies with all applicable regulations.
Best practices for handrail installation include using durable materials like steel or wood, ensuring proper anchoring to the supporting structure, providing continuous handrails without interruptions, and maintaining adequate clearance between the handrail and the wall. Remember, a handrail's effectiveness hinges on its proper installation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Increased Costs |
| Improved Accessibility | Complexity |
| Legal Compliance | Potential Over-Regulation |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Where can I find the building codes for my area? Contact your local building department or access them online.
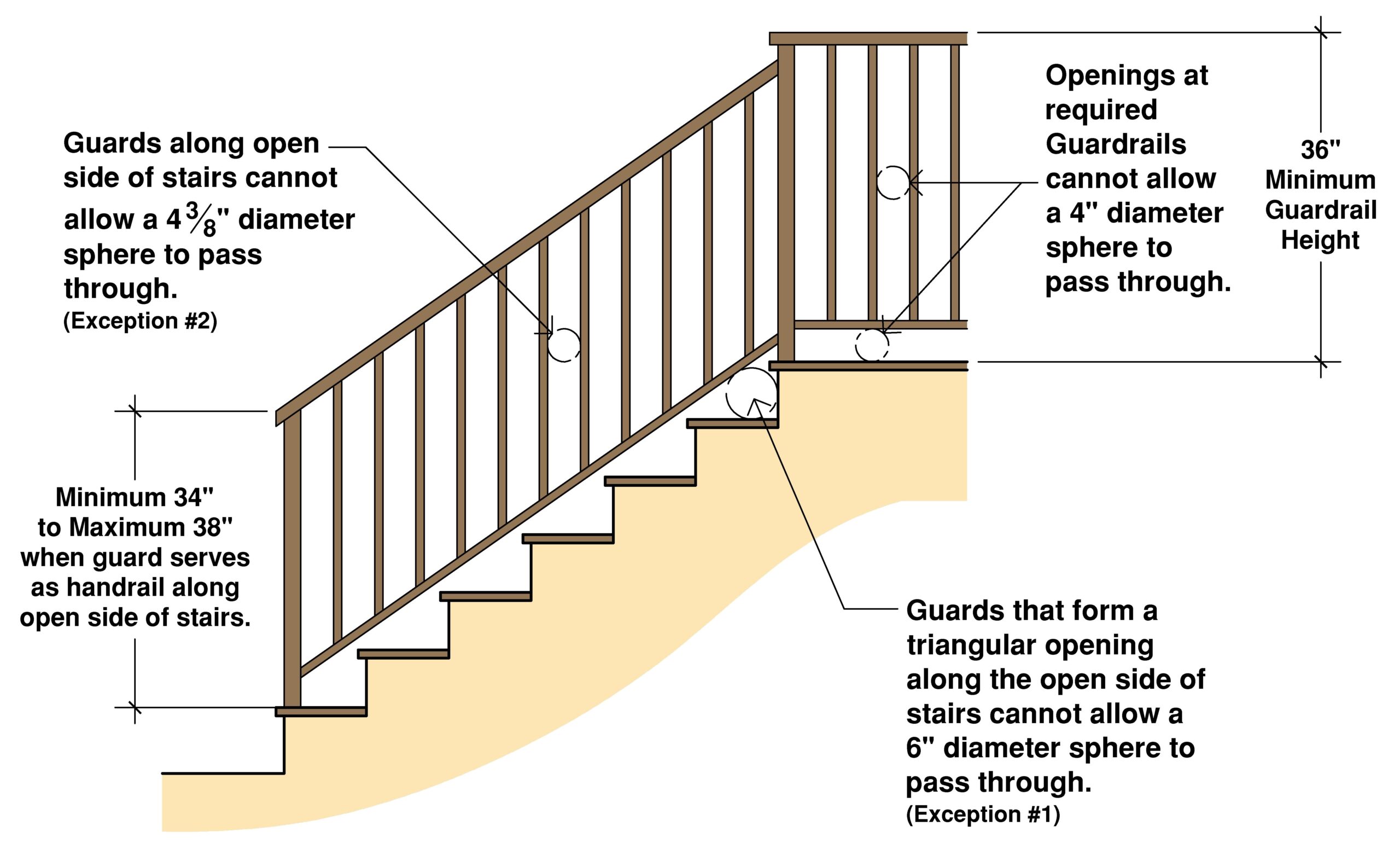
2. What is the standard height for a handrail? Typically between 34 and 38 inches.
3. Do handrails need to be continuous? Generally, yes, with some exceptions.
4. What materials can be used for handrails? Common materials include wood, metal, and composite materials.
5. Can I install a handrail myself? Yes, but it's important to understand the codes and ensure proper installation.
6. What are the consequences of not complying with handrail codes? Fines, legal action, and potential safety hazards.
7. How often should handrails be inspected? Regularly, to ensure they remain in good condition.
8. Where can I learn more about handrail building codes? The International Code Council (ICC) website is a good resource.
Handrail codes, though sometimes complex, serve a crucial purpose. They ensure that the simple act of grasping a handrail doesn't become a risky endeavor. From preventing falls to providing accessibility, these codes contribute to safer and more inclusive environments. By understanding and adhering to handrail building codes, we can create spaces where everyone can navigate with confidence and security. Understanding and implementing handrail codes is crucial for safety and accessibility. By prioritizing these regulations, we create environments where everyone can move with confidence and security. So next time you see a handrail, remember, it's not just a railing; it's a symbol of thoughtful design and a commitment to safety. Take the time to understand and implement these vital regulations, contributing to safer, more accessible spaces for everyone.
The rise of dark fantasy villainy
Unlocking the road exploring the toyota rav4 primes impressive electric range
Unleash the power of behr charcoal blue n490 5

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)