Ever tripped on a staircase and grabbed for a handrail that just wasn't there? Or maybe one that was so low it offered no real support? The seemingly mundane world of handrail heights is actually a critical component of home safety, governed by specific building codes designed to prevent falls and injuries.
Residential handrail height regulations aren't arbitrary; they're based on years of research and analysis of fall patterns and human biomechanics. These codes dictate the required height of handrails on stairs and ramps, aiming to provide secure and comfortable support for anyone ascending or descending.
Understanding residential handrail regulations is essential for both homeowners and builders. Compliance ensures safety for residents and visitors, avoids potential legal liabilities, and contributes to the overall value and quality of a property. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to unsafe conditions and potentially devastating consequences.
Navigating the world of handrail heights can seem complicated, but this guide breaks down the essentials, explaining the reasoning behind the regulations, providing practical tips for implementation, and exploring the potential pitfalls of non-compliance.
From the history of handrail regulations to the latest best practices, we'll unravel the complexities of this critical safety feature. Get ready to elevate your understanding of handrail heights and ensure your home is a safe haven.
The importance of appropriate handrail heights has been recognized for centuries, albeit informally. Early building practices often incorporated handrails for support, though standardization was lacking. The formalization of building codes emerged with the increasing complexity of construction and the growing need for consistent safety standards. Handrail height requirements evolved alongside other building regulations, reflecting an evolving understanding of human factors and accident prevention. Today, these regulations address crucial safety concerns, aiming to minimize the risk of falls, especially among children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility challenges.
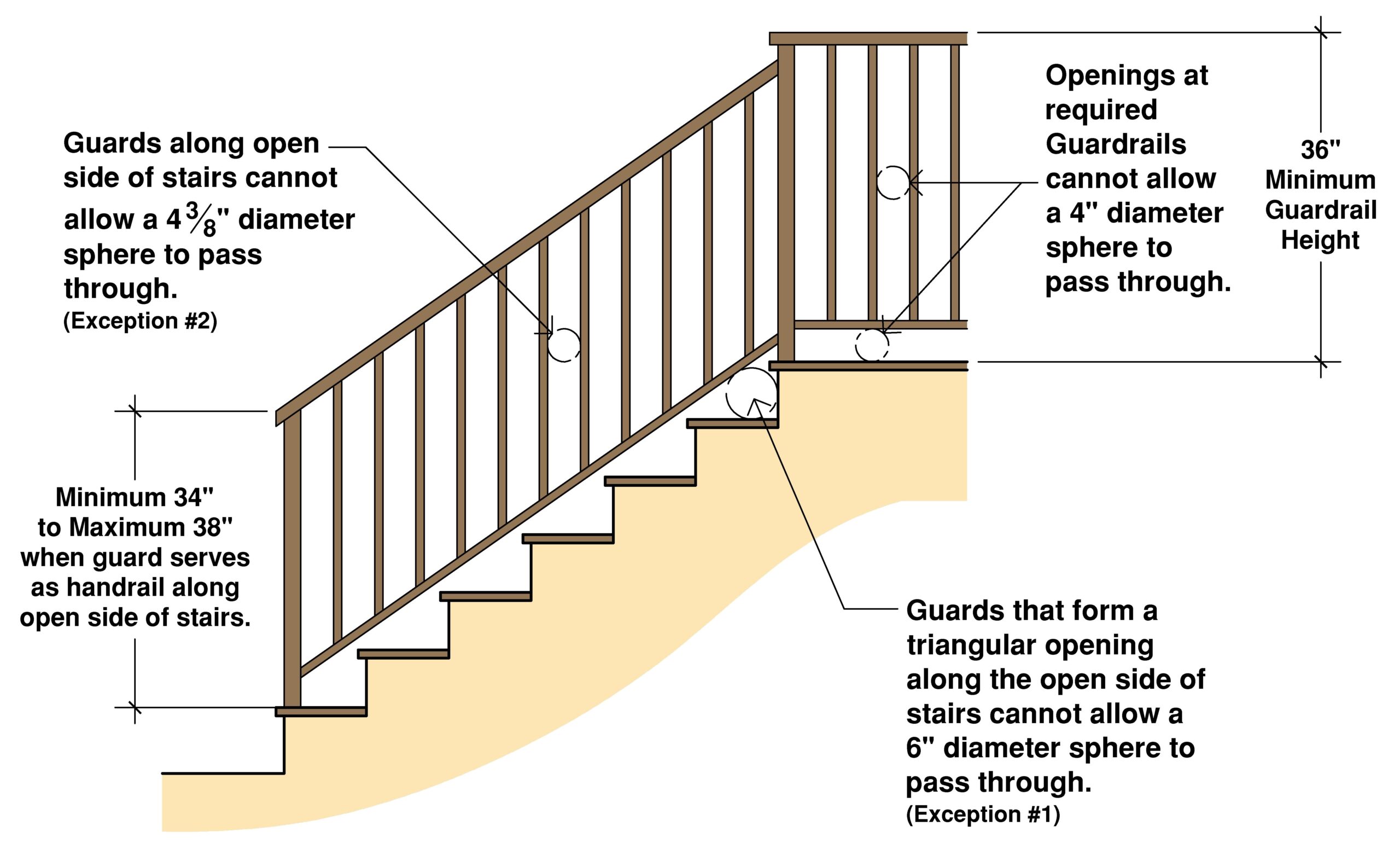
Residential handrail codes specify the minimum and maximum height of handrails measured vertically from the nosing of the stair treads or the ramp surface. These regulations typically require a handrail height between 34 and 38 inches. For example, a handrail installed at 36 inches meets the standard requirement in most jurisdictions. Local building codes can have slight variations, so always check with your local authorities for precise requirements.
Benefits of compliant handrail heights include increased safety, improved accessibility, and enhanced property value. Properly installed handrails reduce the risk of falls, providing a secure grip and preventing loss of balance. They also improve accessibility for individuals with mobility limitations, making it easier to navigate stairs and ramps. Furthermore, adhering to building codes enhances a property's value, demonstrating a commitment to safety and quality construction.
When installing handrails, ensure accurate measurements, secure anchoring, and consistent height throughout the stairway or ramp. Use appropriate materials and follow manufacturer instructions for installation. Regularly inspect handrails for damage and make necessary repairs promptly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Following Handrail Height Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Initial Cost of Implementation |
| Improved Accessibility | Potential Aesthetic Limitations (depending on design preferences) |
| Increased Property Value | Time Investment for Proper Installation |
Best practices include using durable materials, ensuring proper anchoring, consistent height, and regular inspections. Additional practices encompass considering user needs, providing continuous handrails on both sides of stairways, and consulting with local building inspectors for specific requirements.
Challenges can include working with unusual stairway designs, accommodating specific user needs, and interpreting complex code requirements. Solutions involve consulting with architects or experienced builders, seeking customized handrail solutions, and engaging with local code officials for clarification.
FAQ: What is the standard handrail height? What materials are acceptable for handrails? Where can I find my local building codes? What happens if my handrail height is not compliant? Who is responsible for ensuring handrail compliance? Can I install handrails myself? What are the penalties for non-compliance? How often should I inspect my handrails?
General answers to the FAQs would direct readers to consult their local building codes, qualified professionals, and relevant regulatory bodies.
Tips and tricks include using a level to ensure consistent height, pre-drilling holes for anchors, and opting for handrail designs that complement the overall aesthetic of the home.
In conclusion, adhering to residential building codes for handrail height is paramount for ensuring the safety and accessibility of your home. These regulations are not mere formalities; they represent carefully crafted guidelines designed to prevent falls and injuries. By understanding the importance of compliant handrail heights, implementing best practices, and staying informed about local regulations, homeowners and builders can create safer and more accessible living environments. Remember, a small investment in proper handrail installation can yield substantial returns in terms of safety, accessibility, and peace of mind. Take the time to review your handrail heights, ensure compliance, and contribute to a safer environment for everyone. Don't compromise on safety – invest in compliant handrails today. Your future self will thank you.
Uncovering the ancient origins of surfing
Unlocking the secrets of the jackerman mothers war trivia phenomenon
Beat the heat find your local car air conditioning recharge