Navigating stairs safely is a fundamental aspect of accessibility and fall prevention, especially for children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility challenges. Handrails provide crucial support and stability, and understanding the relevant building codes is paramount for both safety and compliance. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of handrail codes for steps, providing you with the knowledge to create safe and accessible environments.
Imagine a world without standardized handrail regulations – inconsistencies in height, materials, and overall design would create hazardous conditions. Handrail codes for steps exist to prevent such scenarios. They establish minimum requirements for handrail design and installation, ensuring consistency and promoting safety on staircases in various settings, from residential homes to commercial buildings.
The history of handrail codes is intertwined with the development of building codes themselves, evolving over time to address emerging safety concerns and advancements in construction techniques. Early regulations focused on basic structural integrity, while modern codes delve into more nuanced aspects like ergonomics, accessibility, and specific requirements for different occupancy types. The specific origins and evolution of handrail regulations can vary depending on the region or country.
The importance of adherence to these codes cannot be overstated. They play a vital role in preventing falls, reducing the severity of injuries, and ensuring accessibility for all individuals. Failure to comply with handrail codes can result in serious consequences, including legal liabilities, costly renovations, and, most importantly, compromised safety.
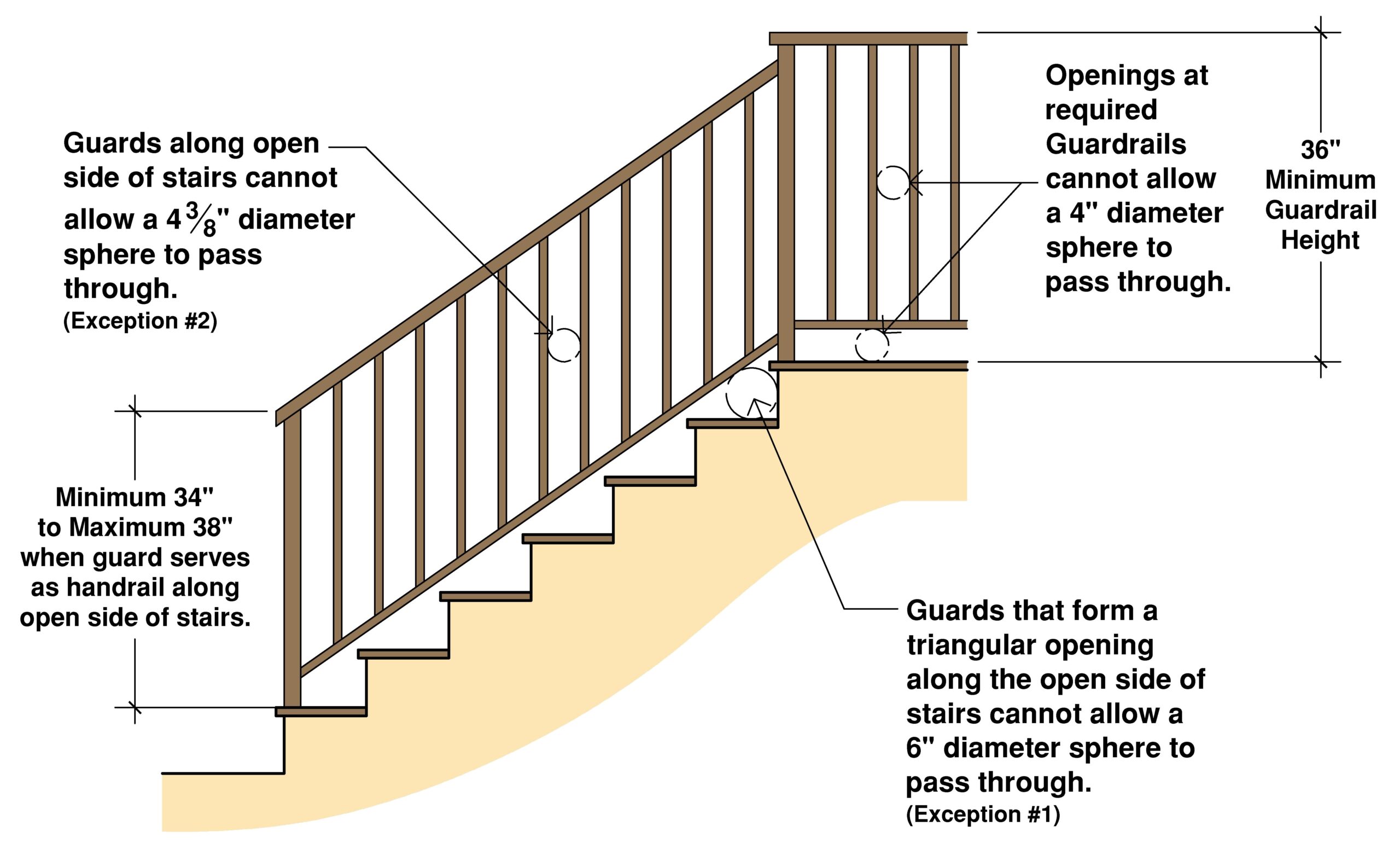
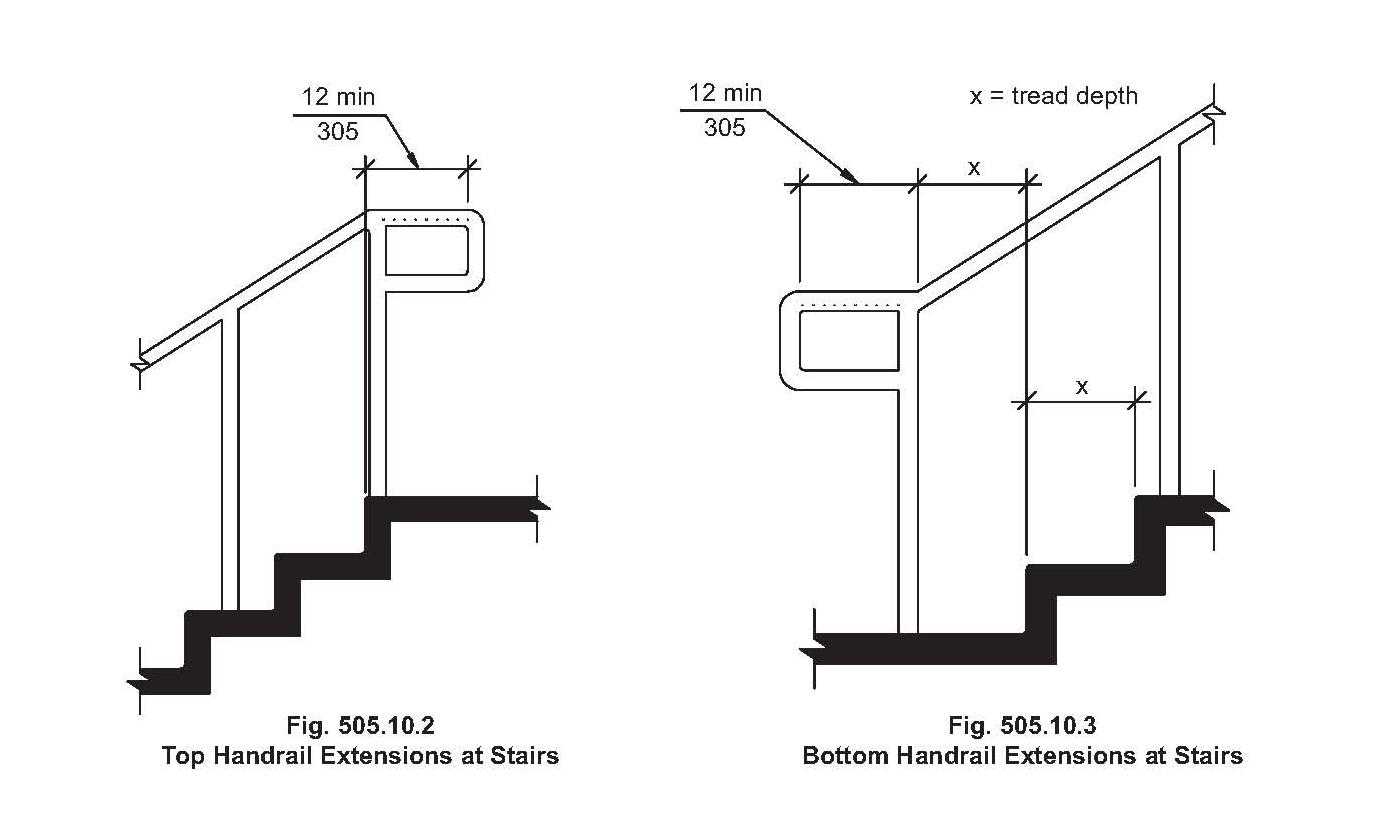
Common issues related to handrail codes for steps include improper height, insufficient gripping surface, inadequate extensions at the top and bottom of the stairs, and lack of continuous handrails on both sides of the stairway. Understanding these common pitfalls is crucial for ensuring compliance and maximizing safety.
Handrail codes typically specify requirements for dimensions, materials, and installation methods. For instance, handrail height is usually measured from the nosing of the stair tread to the top of the gripping surface. Materials should be sturdy and provide a firm grip, and installation must be secure to withstand anticipated loads.
Benefits of adhering to handrail codes include increased safety, improved accessibility, and enhanced compliance with building regulations. For example, properly installed handrails can prevent falls, particularly for individuals with mobility limitations, making stairways safer for everyone. Adhering to code also ensures that your property meets legal requirements, avoiding potential penalties.
Creating a safe staircase involves careful planning and execution. Start by consulting your local building codes to determine the specific requirements for your area. Then, select appropriate materials and engage qualified professionals for installation. Verify the installation against the code requirements to ensure compliance and optimal safety.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potential Cost Increases for Complex Designs |
| Improved Accessibility | Can Limit Design Flexibility in Some Cases |
| Legal Compliance | May Require Specialized Expertise for Interpretation and Implementation |
Best practices include using durable materials, ensuring proper handrail height, providing continuous handrails, extending handrails beyond the top and bottom steps, and regularly inspecting handrails for damage.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the standard handrail height? (Answer: This varies by jurisdiction, consult your local building code.)
2. What materials are acceptable for handrails? (Answer: Typically wood, metal, or composite materials that provide a firm grip.)
3. Do I need handrails on both sides of the stairs? (Answer: Usually, yes, especially for wider staircases. Check local codes.)
4. How far should handrails extend beyond the top and bottom steps? (Answer: Specific measurements are outlined in building codes.)
5. Can I install handrails myself? (Answer: While possible, professional installation is often recommended for ensuring code compliance.)
6. What are the penalties for not complying with handrail codes? (Answer: This can range from fines to mandatory renovations.)
7. Where can I find my local handrail codes? (Answer: Check your local government's building department or website.)
8. Are there exceptions to handrail codes? (Answer: Some exceptions may exist for specific circumstances, but it's crucial to consult local authorities.)
Tips and tricks for working with handrail codes include consulting with experienced builders, using online resources to access code information, and carefully documenting the entire process for compliance verification.
In conclusion, adhering to handrail codes for steps is not merely a legal obligation but a fundamental responsibility for ensuring the safety and accessibility of our built environments. By understanding the codes, implementing best practices, and staying informed about updates and changes, we can create spaces that prioritize the well-being of all individuals. Take the time to review your current handrails, consult local codes, and make any necessary improvements to ensure compliance and enhance safety. Investing in proper handrails is an investment in the well-being of your family, visitors, and community. Remember, a secure handrail is more than just a building component; it's a symbol of care and responsibility.
Unlocking fc 24 smart savings strategies
Understanding a 1 4 reverse stock split
Unlocking the thrills of miniature explosions toy cannons