Ever wonder how that coffee maker pulls a perfect shot of espresso or how those packaged snacks stay fresh for so long? The answer often lies in the ingenious workings of the vacuum pump. This essential piece of equipment, found in countless applications across industries, manipulates pressure to create a vacuum, enabling a range of processes from food preservation to scientific research. Understanding the vacuum pump working principle is key to appreciating its versatility and impact on our modern world.
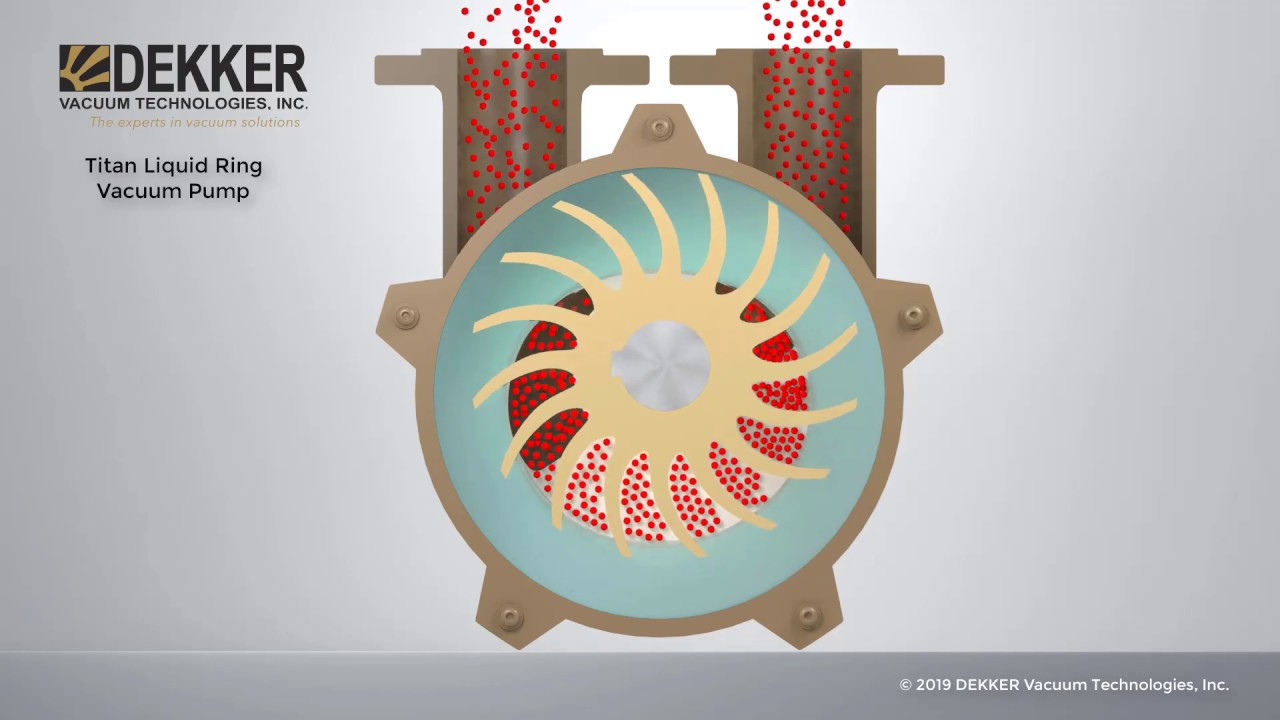
At its core, a vacuum pump operates by removing air and other gases from a sealed space, thereby reducing the pressure within that environment. This pressure difference, compared to the surrounding atmospheric pressure, is what constitutes a vacuum. Different vacuum pump methodologies achieve this pressure reduction through various mechanisms, including positive displacement, momentum transfer, and entrapment. The specific method employed dictates the ultimate vacuum level achievable and the application suitability.
The history of vacuum pump operation traces back centuries, with early experiments paving the way for modern technology. Otto von Guericke's famed Magdeburg hemispheres experiment vividly demonstrated the power of vacuum, while later advancements led to the development of more sophisticated pumps capable of achieving higher vacuum levels. These developments revolutionized scientific research, enabling experiments previously impossible under atmospheric conditions. The significance of vacuum technology continues to grow, driving innovation in fields like medicine, manufacturing, and aerospace.
One of the primary concerns when dealing with vacuum pump functionality is maintenance and troubleshooting. Leaks, worn seals, and contaminated oil can all compromise the system's effectiveness, reducing vacuum levels and potentially damaging the pump itself. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and leak detection, is crucial for optimal performance. Understanding the intricacies of the vacuum pump's working principles is essential for effective troubleshooting and preventative maintenance.
Several distinct categories of vacuum pumps exist, each employing a unique method to achieve vacuum creation. Rotary vane pumps utilize rotating vanes within a cylindrical chamber to displace air. Diaphragm pumps employ a flexible diaphragm to create a pumping action, while diffusion pumps rely on the momentum transfer of a high-speed vapor jet to remove gas molecules. Selecting the appropriate pump type depends on the desired vacuum level, the application's specific requirements, and the properties of the gases being evacuated.
Benefits of effective vacuum pump operation include extended shelf life of food products, enabling global trade and reducing food waste; creation of controlled environments for scientific experiments and industrial processes, and facilitating advanced medical procedures like vacuum-assisted delivery and surgical suction. These examples highlight the multifaceted nature and broad impact of vacuum technology.
A successful vacuum system implementation necessitates careful planning and consideration. Start by defining the required vacuum level and the specific application needs. Next, select the appropriate pump type and size based on these requirements. Ensure proper installation, including leak-free connections and appropriate power supply. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential for long-term performance and reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum Pumps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Wide range of applications | Maintenance requirements |
| Precise control of pressure | Potential noise and vibration |
| Enhanced product quality and preservation | Initial cost investment |
Frequently Asked Questions about Vacuum Pump Working Principles:
1. What is the basic principle behind a vacuum pump? A vacuum pump removes air and other gases from a sealed space, reducing the internal pressure.
2. What are the different types of vacuum pumps? Common types include rotary vane, diaphragm, and diffusion pumps.
3. How do I choose the right vacuum pump for my application? Consider the desired vacuum level, the application's specific requirements, and the gas properties.
4. What is the importance of regular maintenance? Maintenance ensures optimal performance, prevents breakdowns, and extends the pump's lifespan.
5. What are some common troubleshooting issues? Leaks, worn seals, and contaminated oil are common issues.
6. How can I improve the efficiency of my vacuum pump system? Regular maintenance, leak detection, and proper system design can improve efficiency.
7. What safety precautions should I take when operating a vacuum pump? Proper ventilation, eye protection, and handling of potentially hazardous materials are essential.
8. What are some future developments in vacuum pump technology? Research focuses on improved efficiency, reduced noise, and environmentally friendly designs.
In conclusion, understanding the vacuum pump working principle is crucial for harnessing the power of this versatile technology. From food preservation and scientific advancements to industrial processes and medical applications, vacuum pumps play an indispensable role in shaping our world. By grasping the fundamental principles of operation, maintenance best practices, and the diverse range of available pump types, we can effectively leverage the power of vacuum to improve processes, enhance product quality, and drive innovation. Continued exploration and development in this field promise further advancements and applications, solidifying the importance of vacuum technology in the years to come.
Conquering the california dmv test your ultimate guide
Elevate your footwear game jcpenney shoes online
Accessing justice in morris county nj court documentation